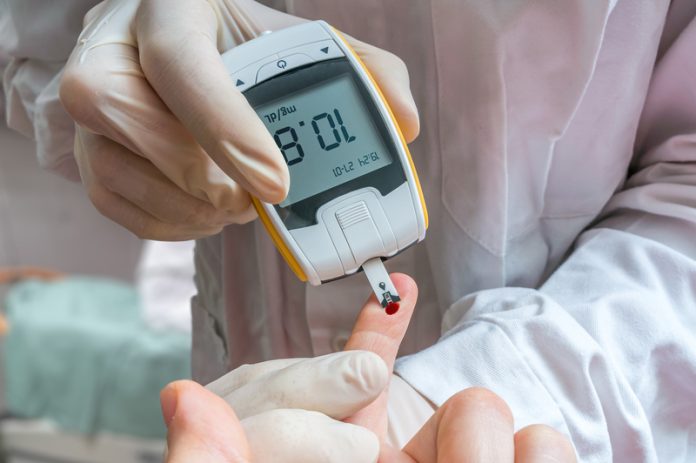
Cecilia Van Cauwenberghe from Frost & Sullivan’s TechVision Group provides a market perspective on the diabetes monitoring and drug delivery innovation fields and explains why these are a scenario for big technology synergy
The diabetes drug delivery market reached over $67 billion in 2017 and is expected to reach at least $120 billion by 2020, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 12.1% from 2017 to 2022. According to Frost & Sullivan studies, inhalable and transdermal delivery present the most impressive growth with a combined CAGR of 27.3%. In particular, inhalable delivery alone exhibits a CAGR of 70.8% for 2015, with an expected global market of $1.6 billion expected by 2020 (Rajan, 218).
Regarding diagnostics, mHealth monitoring systems account for the greater share by taking up 60% of the market. Large pharmaceutical and medical companies, small and medium enterprises (SMEs) and start-ups led by technology entrepreneurs are envisioning significant opportunities to deliver diabetes care innovations, based on decentralised, point-of-care, artificial intelligence (AI)-driven data, to the market, aiming to promote healthy lifestyles and improve treatment outcomes. Private investors, including venture capital firms, have augmented their investments in such therapeutic areas during the past five years, focusing primarily on digital health. These approaches strongly promote a patient’s engagement, thanks to the combination of Big Data analytics and machine learning approaches with smart delivery systems and wearable monitoring devices, committed to precision medicine achievements.
Innovative scenarios
The innovation scenarios can be categorised as follows (Van Cauwenberghe, 2016):
Smart therapeutics
Pharma/biotech innovations in: anti-diabetics, alternative route insulins, insulin analogues, diabetes-related diseases and incretin hormones.
Examples are: Afrezza® (Sanofi and MannKind), Tanzeum® (GSK), Xigdou XR (AstraZeneca), Xultophy® (Novo Nordisk), Smart Insulin (Merck) and Bile Acid Microcapsules (Curtin University).
AI-driven precision medicine
Medtech innovations in: smart insulin pumps, artificial pancreas, glucose monitoring, mobile data analysis, point-of-care devices.
Examples are: FreeStyle® Libre flash glucose monitoring system (Abbott); Contact lens glucose monitoring (Google and Alcon-Novartis); Hidden needles (MIT); Autoantibody measuring chip (Stanford University and IGI Stat); SmartGuard® GlucoSitter Artificial Pancreas Software (Medtronic/DreaMed Diabetes); iLet Bihormonal Bionic Pancreas (Boston University and Massachusetts General Hospital); ITCA 650 (Intarcia), a matchstick-sized transdermal device; and G-Pen Mini(TM) (Xeris Pharma), a pre-mixed glucagon administrator.
Technology convergence
Synertech Innovation in are: micro/nanotechnology, advanced electronics, implantable devices, 3D tissue printing, cell-based therapies (Buch et al., 2018).
Examples include: Glucose sensors with nanoscale components, such as metal nanoparticles and carbon nanostructures for continuous in-vivo glucose monitoring (University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill); spherical nucleic acids silencing gene that interferes with wound healing (Northwestern University); cell reprogramming via nanotechnology for Type 1 diabetes (Southern Medical University in Guangzhou); engineering β-cell replacement therapy (Mayo Foundation for Medical Education and Research); glucose-responsive insulin-producing liver (Orgenesis); and 3-D bioplotted hydrogel scaffolds for islets of Langerhans transplants (University of Twente, Leiden University Medical Center and University Medical Center Utrecht).
Smart Manufacturing
Novel diagnostics and monitoring systems demand for smart specialisation and open or semi-open manufacturing systems, in order to exploit the huge potential of mHealth, AI-driven systems to accelerate technological progress in diabetes care. According to experts, these combined factors are expected to lead to a cascading effect on the productivity and efficiency of health systems with a technological base (Doupis et at.,2018).
Advanced manufacturing is witnessing an increasing amount of intelligent new processes and solutions in the glucose monitoring value chain, therefore, savings costs, reducing time and providing much better quality production (Contreras and Vehi, 2018). This approach directly impacts the whole value chain by offering more flexible, agile and efficient manufcaturing processes.
Final remarks
Demand is increasing for more personalised and precision medicine in diabetes- and cardio-metabolic related diseases. As a result, diverse elements throughout the biomedical production process are appearing on the scene. Parallel trends in biotechnolohy, including stem cell therapies, are occuring with the advent of personalised biomarkers which are reshaping the diabetes and cario-metabolic fields.
Similarly, the combination of advanced diagnostics and monitoring technologies with smart materials and flexible electronics are revealing a very promising synergy. The market is clearly reflecting these investigational trends with the introduction of new commercially-available monitoring, testing, wearables and portable products, many of them behaving as intelligent medical devices. An important acceleration of these trends is expected within the next two years.
Acknowledgements
I would like to thank all contributors from industry involved with the development and delivery of this article from the TechVision Group at Frost & Sullivan.
References
- Buch, V., Varughese, G. and Maruthappu, M., 2018. Artifical intelligence in diabetes care. Diabetic Medicine, 35(4), pp.495-497
- Contreras, I. and Vehi, J., 2018. Artificial intelligence for Diabetes Management and Decision Support: Literature Review. Journal of medical internet research, 20(5)
- Doupis, J., Papandreopoulou, V., Glykofridi, S. and Andianesis, V., 2018. Mobile-Based Artificial Intelligence Significantly Improves Type 1 Diabetes Management.
- Rajan, B., 2018. Breakthrough Innovations in PoC Diagnoses for Smart Healthcare. Frost & Sullivan TechVision Analysis. D817.
- Van Cauwenberghe, C., 2016. Next-generation Technologies for Diabetes Therapy and Drug Delivery – Depicting the Perfect Scenario for Cutting-Edge Technology Convergence in Biomedical Sciences. Frost & Sullivan TechVision Analysis. D6D9.
Cecilia Van Cauwenberghe
PhD, MSc, BA Associate Fellow
and Senior Industry Analyst
TechVision Group, Frost & Sullivan
Editor's Recommended Articles
-
Must Read >> Tackling chronic diseases through innovative health
-
Must Read >> Keeping watch: The story of a diabetes service dog