Aarthi JanakiRaman, Research Director, Chemicals and Advanced Materials at TechVision, charts the rising importance of soil health for sustainable agriculture
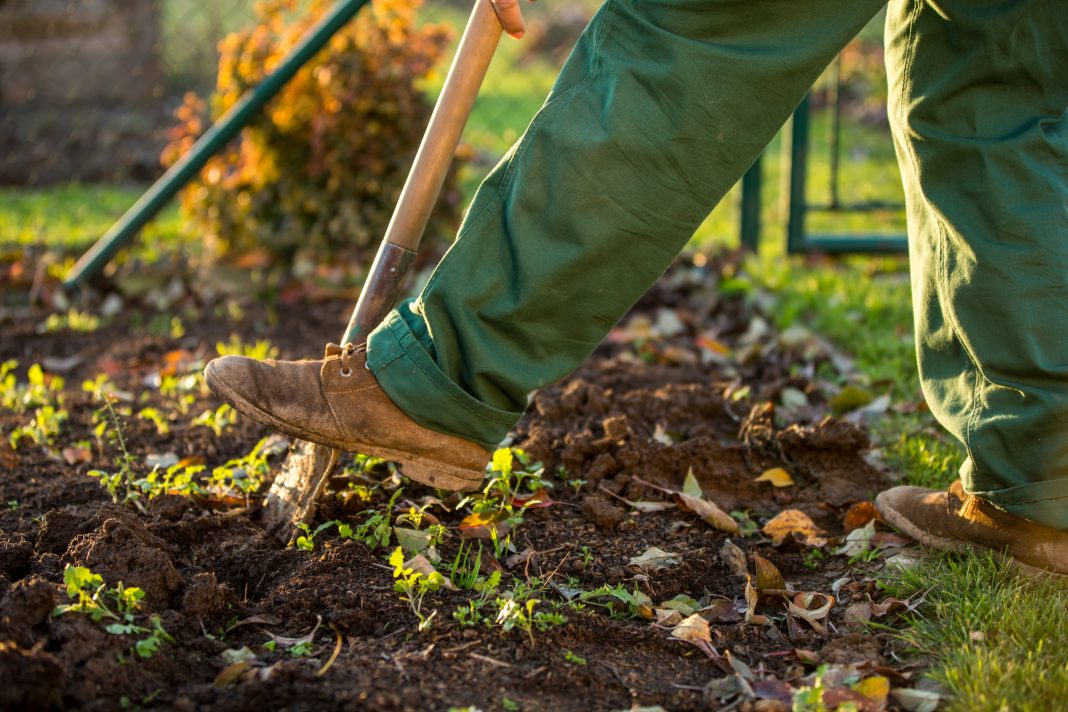
The ever-expanding global population has resulted in the growing importance of agriculture to ensure food security for people in all walks of life. The ever-rising intensity of agricultural activities involves the use of varied agricultural inputs to increase yield and production and shorten the crop cycle to meet demand. While the intensification of activities has enabled demand to be met at an optimal level, it has also resulted in a change in the soil ecosystem leading to changes in the biotic and abiotic factors that nourish and replenish the soil ecosystem and soil health. This, in turn, increases the requirement for agricultural inputs such as fertilizers and pesticides to ensure the required yield, which further causes changes in the soil ecosystem, leading to a vicious cycle of depletion of the indigenous soil biota.
A growing focus on sustainability has resulted in an evaluation of agricultural activities and their contribution to climate change. Various studies have underlined the potential environmental degradation that had resulted in the reduced nutrient availability to crops and increased susceptibility to environmental stresses and pathogens. Hence, sustainable agriculture is gaining prominence not only to preserve and replenish the soil ecosystem, but also as a way to mitigate climate change and be in compliance with the Sustainable Development Goals.
Sustainable agriculture involves interconnected activities that are linked in various points of the plant lifecycle and soil management, with an underlying aim to implement a crop production and protection ecosystem that doesn’t involve environmental degradation while maximizing yield and productivity. Various facades of the soil ecosystem act as key influencers for increasing sustainability, which, in turn, makes inroads in protecting our environment and mitigating climate change effects; be it farming practices to types of pest control solutions and fertilizers used. It’s important to pay attention to each individual part of agricultural activities, while considering the entire agricultural ecosystem to help in promoting sustainability.
Soil health and its role in sustainability
Soil quality is a key determinant of sustainable agriculture that is influenced by the various physical and chemical properties whilst considering the influence of climate and external inputs. Various current land and crop management practices have resulted in degradation of soil quality, thereby, adversely impacting the sustainability of agricultural inputs. For example, excessive use of fertilizers has resulted in a nutrient surplus in parts of the world, resulting in water and air pollution, and disturbing human health and the environment. On the other hand, an imbalance in the supply of nutrients can reduce soil fertility and organic matter, affecting the soil microbiota and resulting in erosion. A healthy soil ecosystem involves design and management to maintain a healthy and sustainable ecosystem that is not limited to nutrient cycling, biological control of biotic and abiotic factors and regulation of water and air supply.
Many approaches are considered to reverse the changes of reduced soil quality while trying to replenish them. United Nations Convention to Combat Desertification (UNCCD) recommends systematic conservation agriculture practices that integrate crops with livestock and trees to create a healthy and complementary ecosystem. Approaches such as switching to biological plant growth agents instead of synthetic ones, and an integrated approach to water and soil management are also being pursued. An emerging approach, established by several research activities, is that use of carbon sequestration will have a positive impact when it comes to promoting a healthy soil ecosystem. Apart from increasing the soil quality and promoting plant growth, it can increase water availability to plants, reduce the impact of pollutants and improve soil and plant resilience to external environmental conditions.
It’s also equally important to establish preventive measures to prevent further degradation of soil. A comprehensive action plan is needed to implement soil-friendly processes on a global scale. This requires the involvement of stakeholders across all societal segments, including farmers, researchers, trade associations, industrial participants, and the public. Development of qualitative and quantitative indicators that can continuously monitor soil health and help in developing/modifying an intervention plan to improve the nutrient content, soil microbiota, access to water and air can go a long way in maintaining soil health. Tax credits, financial aid and legislation that encourage the adoption and long-term implementation of soil friendly practices can help farmers choose agricultural inputs that don’t harm the soil while replenishing it.
“A growing focus on sustainability has resulted in an evaluation of agricultural activities and their contribution to climate change. Various studies have underlined the potential environmental degradation that had resulted in the reduced nutrient availability to crops and increased susceptibility to environmental stresses and pathogens.”
The role of soil microbiota is also crucial for establishing sustainable agricultural practices. Treating the soil ecosystem as a diverse food web and regulating the growth of beneficial microbes and plant pathogens can help in establishing a healthy soil microbial population that can help in promoting plant growth and yield but also help in maintaining healthy soil. Soil microbiota is often used as an indicator for soil health; hence, careful selection of growth promoters, plant protection agents, and microbial inoculants that are of biological origin causes minimal impact on the soil ecosystem as opposed to chemically derived ones. Further, they can also help in water conservation and improve water availability to plants.
The final word
Understanding the role of various agricultural practices is essential to promoting sustainable agriculture. Integration of conventional practices with a modern approach can help in establishing sustainable agriculture while ensuring the requisite yield, and productivity and integrated farm and pest control solutions are key to maintaining good soil health.
It’s an established fact that the health of soil, plants, animals, humans and the environment are all interlinked and an imbalance of one affects the rest. For a sustainable economy, it’s important to maintain a soil-human-environment nexus that includes complete management of all interconnected activities that will provide long-term benefits and help towards the transition of a sustainable economy.
Extra focus: A look at Canadian agriculture
Supporting the Canadian agriculture and agri-food sector through initiatives that foster competitiveness and innovation sum up the mission of Agriculture and Agri-Food Canada. (1) The Honourable Marie- Claude Bibeau, MP, current Minister of Agriculture and Agri-Food (2), showed her support in mid-August for Canadian farmers who are crucial in the effort to build a more sustainable agricultural sector in the Country. “By innovating and adopting sustainable agricultural practices, Canadian producers are demonstrating their commitment to reducing our GHG emissions. To help them do this, and as part of the Agricultural Climate Solutions program, we have selected Perennia to administer an $8.5-million fund in Nova Scotia and Newfoundland and Labrador,” Minister Bibeau explains. (3)
It’s interesting to observe a story about how young Canadians will shape the agriculture and agri-food sector in the years ahead, and as such, their voice must be heard. “Young people’s perspectives on issues such as sustainable agriculture, innovation, intergenerational transfers, mental health and work-life balance allow us to shape the sector’s future in their image,” Minister Bibeau affirms. (4)
The Government of Canada’s investment of $1.8 million to accelerate bioeconomy growth in the agriculture sector was heralded in August. “By adding value to products once considered to be waste, and ensuring the quality of these bioproducts through strict quality standards, we will help strengthen Canada’s position as a leader in sustainable agriculture while creating new revenue sources for our agricultural producers,” Minister Bibeau says. (5)
References
1. https://agriculture.canada.ca/en
2. https://www.canada.ca/en/government/ministers/marie-claude-bibeau.html
3. https://www.canada.ca/en/agriculture-agri-food/news/2022/08/government-of-canada-invests-85-million-to-help-farmers-in-nova-scotia-and-newfoundland-and-labrador-adopt-sustainable-practices.html
4. https://www.canada.ca/en/agriculture-agri-food/news/2022/08/minister-bibeau-announces-the-composition-of-the-2nd-cohort-of-the-canadian-agricultural-youth-council.html
5. https://www.canada.ca/en/agriculture-agri-food/news/2022/08/government-of-canada-invests-18-million-in-green-economy.html
Contributor Profile
Editor's Recommended Articles
-
Must Read >> Food allergies: An epidemic in the making?