Open Access Government produces compelling and informative news, publications, eBooks, and academic research articles for the public and private sector looking at health, diseases & conditions, workplace, research & innovation, digital transformation, government policy, environment, agriculture, energy, transport and more.
Home 2026
Archives
Skeletal muscle memory: Recall for healthy aging
Learn about the critical role of skeletal muscle in overall health, and the importance of maintaining muscle mass as we age to support longevity and combat age-related conditions.
Care research: The importance of philanthropy
In this exclusive interview, Dr Benson from the Robert H. Lurie Comprehensive Cancer Center explores the importance of philanthropy and the power it has to drive innovation and collaboration, particularly in cancer research and patient care.
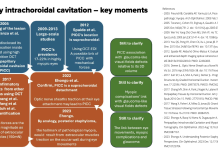
Peripapillary intrachoroidal cavitation and biomechanical considerations: A multi-stage narrative
Dr Adèle Ehongo discusses Peripapillary intrachoroidal cavitation and biomechanical considerations in a multi-stage narrative.
Lithium supplements to prevent Alzheimer’s disease: A poisoned chalice?
Matthew J. Armstrong, Anthony E. Valenzuela, and Pamela J. Lein explore the use of lithium supplements to prevent Alzheimer’s disease and whether this approach is a poisoned chalice.
CoDiet: You are what you eat
Learn about CoDiet, an international research initiative aimed at addressing diet-related diseases using innovative monitoring technologies and personalised nutrition.
How academic-tribal teams cut cancer risks in Native American communities
Learn how the Native American Center for Cancer Health Excellence addresses cancer health disparities through bidirectional research that honors tribal sovereignty.
Modern payment models in health
Oriana Ciani addresses the financial pressures that healthcare payers face due to rising costs of innovative therapies. The HI-PRIX project, funded by Horizon Europe, aims to create adaptable pricing and payment model for health systems, focusing on financial sustainability, supporting innovation, and ensuring timely access to high-cost medicines.
Dynamic feedback modeling to predict random infection outcomes
Brian P. Lazzaro from Cornell University discusses the role of dynamic feedbacks in determining infection outcomes.
Safe and effective use of opioids for co-occurring disorders
Co-occurring disorders and clinical care for complex illnesses- safe and effective use of opioids may be only one of the areas where we need collaboration. Norm Buckley from the Michael G. DeGroote Institute for Pain Research & Care explains.
Mental health in the health workforce
Auckland University of Technology Associate Professor Dianne Wepa’s research found that mental health in the health workforce is influenced by how workplace cultures either promote or hinder psychological safety.
Novel adjunct treatments for posttraumatic stress disorder: Neurofeedback and deep brain reorienting
Dr. Ruth Lanius, Scientist at London Health Sciences Centre Research Institute (LHSCRI) and Psychiatrist at London Health Sciences Centre (LHSC) discusses the need for novel adjunct treatments for posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD), highlighting two promising approaches: neurofeedback and Deep Brain Reorienting (DBR).
The next step in regenerative medicine for osteoarthritis: Spscs and a new regulatory pathway
Osteoarthritis (OA) remains one of the leading causes of disability worldwide, burdening health systems and diminishing quality of life for millions.
Piezo4Spine: Dreaming on a cure for paraplegic patients
Piezo4Spine is a European project that aims to develop a novel therapy to repair the injured spinal cord, a pathology for which a cure remains elusive. María C. Serrano tells us more.
Liver regeneration in alcohol related liver disease
Recompensation in liver disease indicates both a physical and molecular improvement in liver functions. Molecular regeneration is key to improving liver function, and novel technologies in proteomics and RNA transcriptomics may hold the key to advancing liver regeneration in alcohol-related liver disease. Nina Kimer explains.
Indigenous health research program: Offering insights for better health
Dr. Mamata Pandey, Research Scientist at the Saskatchewan Health Authority in Canada shares insights from her Indigenous-partnered health research program, enhancing health.
Wellbalance elevates coaching through the science of personalized wellbeing
WellBalance’s “Wellbeing Balance and Lived-Experiences Model of Positive Wellbeing”, developed by Harvard-trained scientist Troy W. Norris, is the first scientifically validated experiential model of wellbeing.
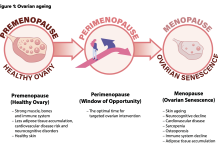
Targeting the perimenopause window to delay ovarian ageing and enhance healthspan
Adjunct Assistant Professor Zhongwei Huang and Dr. Paula Benny discuss perimenopause and ovarian ageing, highlighting the importance of future interventions focused on early detection, personalized treatments, and lifestyle modifications to improve health outcomes and longevity.
Endothelial – The final frontier to reduce preterm birth and death from sepsis
Each year, around 15 million babies are born prematurely, with nearly one million dying soon after due to complications. Maternal mortality remains high, particularly in low-resource settings. This article describes how assessing endothelial integrity and function could help identify at-risk pregnancies to prevent adverse outcomes.
Exploring genetic tools in environmental microbes: Applications in extracellular electron transfer
Arpita Bose and Zhecheng Zhang explore genetic tools in environmental microbes, citing applications in extracellular electron transfer/
Healthy diet for dementia prevention
Contributors from the Jockey Club Centre for Positive Ageing outline dietary strategies that can help preserve cognitive function and prevent dementia.