Open Access Government produces compelling and informative news, publications, eBooks, and academic research articles for the public and private sector looking at health, diseases & conditions, workplace, research & innovation, digital transformation, government policy, environment, agriculture, energy, transport and more.
Home 2026
Archives
Care research: The importance of philanthropy
In this exclusive interview, Dr Benson from the Robert H. Lurie Comprehensive Cancer Center explores the importance of philanthropy and the power it has to drive innovation and collaboration, particularly in cancer research and patient care.
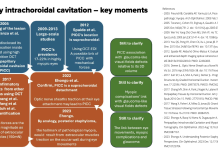
Peripapillary intrachoroidal cavitation and biomechanical considerations: A multi-stage narrative
Dr Adèle Ehongo discusses Peripapillary intrachoroidal cavitation and biomechanical considerations in a multi-stage narrative.
The next step in regenerative medicine for osteoarthritis: Spscs and a new regulatory pathway
Osteoarthritis (OA) remains one of the leading causes of disability worldwide, burdening health systems and diminishing quality of life for millions.
Exploring genetic tools in environmental microbes: Applications in extracellular electron transfer
Arpita Bose and Zhecheng Zhang explore genetic tools in environmental microbes, citing applications in extracellular electron transfer/
Cladoselache, a puzzling ancient shark-like fish
Loren E. Babcock, Professor in the School of Earth Sciences at The Ohio State University, introduces research on Cladoselache, a puzzling ancient shark-like fish.
Can stem cells aid coral reef recovery?
Shani Talice and Benyamin Rosental from Ben Gurion University of the Negev explore how stem cells could help corals recover from stress and environmental damage, addressing the urgent threats of climate change, pollution, and disease to coral reefs.
The science of gamification: Reimagining biomedical education through gamified learning
Dr Michael J. Dillon and Prof Laura Bowater examine the science of gamification to transform biomedical education through gamified learning.
Developmental biology: A self-propagating wave builds skull bones
Interdisciplinary approaches in developmental biology have revealed how cells build the embryonic bones of the skull vault. Spatial and temporal dynamics are coordinated by cells as they build the extracellular environment, Jacqueline Tabler explains.
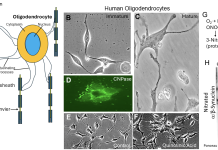
iPSCs and NSCs model newborn brain injury
This article discusses research by Dr. Lee J. Martin and his team on HIE, a leading cause of neonatal mortality. They use human induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) and neural stem cells (NSCs) and emphasize the vulnerability of oligodendrocytes, sharing how these cells can accumulate toxic misfolded proteins, potentially causing severe neural damage and long-term cognitive disabilities in affected infants.
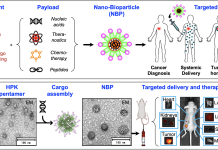
Nano-bioparticles: Fighting cancer with targeted nanotherapy
Dr LK Medina-Kauwe developed a bioengineered delivery system to treat resistant and metastatic tumors, highlighting the potential of nano-bioparticles to enhance cancer therapy by targeting specific tumor characteristics and overcoming treatment barriers.
Smarter decisions, better outcomes: How a new molecular test improves patient care
Oliver Bathe, Professor of Surgery and Oncology at the University of Calgary and CEO of Qualisure Diagnostics, examines how a new molecular test can lead to smarter decisions and better patient care outcomes in his third article.
Gut microbiome and aging – Unlocking new frontiers in healthy longevity
As the population ages, research into preserving healthy longevity is gaining pace. Christian Brechot highlights the role of the gut microbiome – a complex community of microorganisms within us – in influencing health as we age.
What can we learn from millions of viral genome sequences?
David Ussery and Pratul Agarwal, Professors in the Department of Physiological Sciences at Oklahoma State University, discuss their work using high-performance computing for the analysis of millions of viral genome sequences.
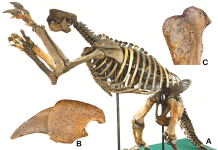
A gentle giant: Thomas Jefferson’s ground sloth
Professor Loren E. Babcock and Dr H. Gregory McDonald discuss the historical significance of palaeontology, focusing on key figures’ contributions to the field and their studies of the ground sloth, Megalonyx.
The next chapter in regenerative medicine for osteoarthritis: From real-world evidence to regulatory shifts
Osteoarthritis (OA) remains one of the leading causes of disability worldwide, yet the therapeutic landscape is evolving faster than ever.
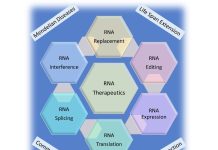
The oncoming tsunami of RNA therapeutics
Alan Herbert, Founder and President of InsideOutBio, discusses the significant advancements in RNA therapeutics, highlighting their role in supporting public health and their transformative potential in modern medicine, particularly for addressing genetic conditions and cancer.
Enabling preventive medicine and improving patient care via aptamer-based molecular monitors
As health systems put greater focus on preventive, personalized care, Netzahualcóyotl Arroyo-Currás tells us about the broad benefits of Continuous Molecular Monitors (CMMs) in providing insights into biomolecular markers that facilitate early disease detection.
Deconstructing misconceptions: The relevance of androgens for human health
Alexandra Cara and Carol F. Elias from the University of Michigan Medical School provide insights into the critical role of androgens in human health, including their vital roles throughout various life stages.
Unravelling NASH and insulin resistance: Insights from the department of human health and nutritional...
Open Access Government sits down with a researcher from the Department of Human Health and Nutritional Sciences to discuss their groundbreaking work on nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) and insulin resistance. Their research delves into the molecular underpinnings of these increasingly prevalent conditions, offering new avenues for understanding, prevention, and treatment.
Asbestos: Early immune responses
Ujjwal Adhikari, Kinta Serve, and Jean Pfau explain how asbestos exposure negatively affects the body’s immune response and repair mechanisms, particularly through macrophage dysfunction. They emphasize that gaining a better understanding of cellular responses to inhaled particles could help researchers discover new therapeutic strategies for addressing environmentally induced conditions.