Open Access Government produces compelling and informative news, publications, eBooks, and academic research articles for the public and private sector looking at health, diseases & conditions, workplace, research & innovation, digital transformation, government policy, environment, agriculture, energy, transport and more.
Home 2026
Archives
Magnetobiology: Beyond attraction
Jinxing Li and Christopher H. Contag delve into the emerging field of magnetobiology, which utilizes magnetic fields to manipulate and control living systems, while reflecting on its potential to surpass the limitations of other modalities.
Berry and honey production in Alberta: Exploring the market system
Aleksandra Tymczak studies the berry and honey industries in Alberta’s agricultural system. Here, she discusses the challenges and opportunities for farmers to access markets, as well as the current capacity for the distribution system across Alberta’s agricultural system.
Care research: The importance of philanthropy
In this exclusive interview, Dr Benson from the Robert H. Lurie Comprehensive Cancer Center explores the importance of philanthropy and the power it has to drive innovation and collaboration, particularly in cancer research and patient care.
Reimagining mining for a net-zero future
Carbon-negative mining offers a promising path to meeting the mineral demands of the energy transition while shrinking the industry’s carbon footprint. In this article, Dr Estibalitz (Esti) Ukar examines how innovative geochemical and geomechanical processes could turn mining into a net-negative carbon industry.
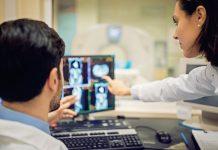
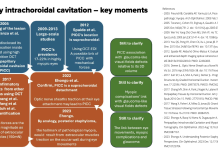
Peripapillary intrachoroidal cavitation and biomechanical considerations: A multi-stage narrative
Dr Adèle Ehongo discusses Peripapillary intrachoroidal cavitation and biomechanical considerations in a multi-stage narrative.
Precycling: Waste to plastics resource pathways
The PRecycling project aims to recover high-quality polymeric materials from underutilized plastic waste streams, focusing on developing near-production-scale recycling processes to transform plastic waste into secondary raw materials, and enabling up to 100% recycled content incorporation in new products.
Does size matter? Guiding deforestation to mitigate Amazonian tipping cascades
The Amazon, a critical global climate tipping element, faces destruction due to land transformation. Research by University of Hamburg and iES Landau investigates whether the size and pattern of deforestation matters, suggesting that guiding clearing can mitigate severe regional climate impacts.
From lecture halls to living labs: Tackling biodiversity loss through nature-based solutions
Learn how to empower higher education and vocational training to address biodiversity loss through Nature-Based Solutions.
Two worlds, one test: Climate leadership after Belém
Professor Richard Beardsworth analyses climate leadership after Belém, focusing on managing the fossil fuel transition beyond COP30.
Longitudinal Educational Achievements: Reducing Inequalities (LEARN) Project
Paula Sergeant from Manchester Metropolitan University and Doris Hanappi from University of Zurich present the Longitudinal Educational Achievements: Reducing Inequalities (LEARN) Project.
Beyond microbial fermentation: Reimagining biomanufacturing for low-resource environments
Although traditional biomanufacturing is based on microbial or mammalian cell culture, plants can be grown in bioreactors and hold enormous promise for use in resource-limited environments.
Vision-controlled plant assessments lead the way to more automation
Vision-based strawberry plant assessments are essential first steps towards increased automation, mitigating periodically high labour demands.
Local governments in Europe play a crucial role in achieving climate neutrality
Alina Safronova at the Institute of Energy Systems and Environment, Riga Technical University, examines how local governments in Europe are one of the most important driving forces on the path to climate neutrality.
Gallium oxide: The race to power the next-generation grid and EV infrastructure
In an exclusive OAG Q&A interview, Professor Singisetti from the Department of Electrical Engineering at the University at Buffalo discusses the commercialisation path for Gallium Oxide in high-power electronics.
Navigating uncertainty: How advanced forecasting builds resilient institutions
Dr Yves R. Sagaert emphasizes the importance of organizations shifting away from traditional static budgeting, which relies on historical trends. He advocates adopting predictive AI and advanced forecasting as essential strategic tools for both governments and businesses to proactively adapt to uncertainties in their environments.
Lithium supplements to prevent Alzheimer’s disease: A poisoned chalice?
Matthew J. Armstrong, Anthony E. Valenzuela, and Pamela J. Lein explore the use of lithium supplements to prevent Alzheimer’s disease and whether this approach is a poisoned chalice.
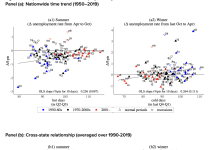
Global warming fuels unemployment rate in summer
Masahiro Yoshida from Waseda University’s Department of Political Science and Economics finds that global warming raises summertime unemployment.
Learning with AI: Losing critical thinking at the worst time
Nancy Butler Songer argues that learning with artificial intelligence is contributing to the erosion of critical thinking skills at a time when it is most needed.
Improving food safety risk analysis for safer European food systems
The HOLiFOOD consortium is reimagining food safety risk assessment for the benefit of all stakeholders in the food chain.
Astronomy: The initial conditions for planet formation
Leonardo Testi, Ugo Lebreuilly, Elenia Pacetti, Anaëlle Maury, Veronica Roccatagliata, Patrick Hennebelle, Ralf Klessen, and Sergio Molinari investigate the initial conditions for planet formation in this special astronomy focus.