Open Access Government produces compelling and informative news, publications, eBooks, and academic research articles for the public and private sector looking at health, diseases & conditions, workplace, research & innovation, digital transformation, government policy, environment, agriculture, energy, transport and more.
Home Search
astronomy - search results
If you're not happy with the results, please do another search
Scientists uncover intermediate-mass black holes
New research offers compelling evidence for intermediate-mass black holes (IMBHs), the "missing links" in black hole evolution. These studies provide unprecedented insights into the universe's earliest stars and galaxy formation, bridging the gap between stellar and supermassive black holes.
Mysterious cosmic object seen flashing in radio waves and X-rays
A team of international astronomers has discovered a mysterious and perplexing cosmic object in our Milky Way galaxy that challenges our current understanding of how stars behave.
New study finds planets can form even under harsh UV radiation
A team of astronomers led by Penn State has discovered that planet-forming materials can survive and persist even in some of the most extreme environments in our galaxy.
Galactic turbulence defies expectations: Scientists uncover new insights
Galactic turbulence, a cosmic enigma influencing everything from star formation to particle movement, has been simulated with unprecedented precision. The surprising results challenge long-held theories about energy flow in the vast interstellar medium.
How did the first stars form in space?
Ralf Klessen, professor of theoretical astrophysics at Heidelberg University, investigates the physical processes that governed the formation of the first generation of stars in the early Universe.
Prof. Dr. Ralf S. Klessen – Heidelberg University
Ralf Klessen is a professor of theoretical astrophysics at Heidelberg University. His research interests range from characterizing the physical processes that govern the birth of stars — both at present and in the early Universe — to gas dynamics and chemistry in the interstellar medium, which fills the space...
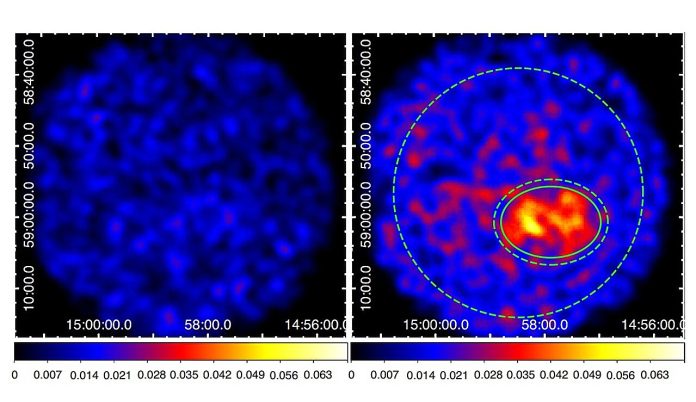
Neutrino mystery in the squid galaxy has a new explanation
The IceCube Neutrino Observatory recently detected something unusual coming from the Squid Galaxy, officially known as NGC 1068.
NASA reveals 3D visualisation of stunning cosmic cliffs
NASA has released a new 3D visualisation of the “Cosmic Cliffs,” a star-forming region captured by the James Webb Telescope (JWST).
X-ray source AX J145732−5901 unmasked as distant galaxy cluster
Scientists have identified a mysterious X-ray source, known as AX J145732−590 located far beyond our own Milky Way. Observations using X-ray telescopes suggest this object, previously hidden by the dense material within our galaxy, is a large collection of galaxies.
AI breakthrough reveals new ways of observing gravitational waves and extreme events
As artificial intelligence helps scientists push the boundaries of how we observe the universe, researchers have developed an AI system capable of designing entirely new types of detectors for observing gravitational waves.
The role of neutrinos, quantum mechanics and special relativity in baryogenesis
Constantinos G. Vayenas from the University of Patras and the Academy of Athens, explores the roles of neutrinos, quantum mechanics, and special relativity in baryogenesis.
UK boosts science and technology ties with the EU
The UK government is trying to strengthen its science and technology ties with the European Union, revealing new plans to enhance cooperation and drive innovation.
The role of neutrinos and Special Relativity in Baryogenesis
It is well known that systems comprising two or more rotating particles or bodies play an important role not only in Astronomy and Chemistry, but also on Nuclear Physics. In Chemistry such systems are known as the Bohr model, whereas in particle physics they are known as the Rotating Lepton Model.
October’s supermoon: Cultural celebrations and celestial wonders
The next full Moon will occur on Thursday, October 17, 2024, at 7:26 a.m. EDT and is filled with celestial and cultural significance, NASA has reported.
Protoplanetary disks: New insights from the James Webb Telescope
Using NASA's James Webb Space Telescope (JWST), astronomers have uncovered details about the processes shaping protoplanetary disks, the cosmic nurseries where planets are born.
The dynamics of soil health
Thomas Gumbricht from Stockholm University and xSpectre, with Sonia Meller from Digit Soil, discuss what we need to know about understanding the dynamics of soil health.
Peter Melchior – Princeton University
Peter Melchior is Assistant Professor of Statistical Astronomy at Princeton University. He leads the Princeton Astro Data Lab, which develops new algorithms to change how astronomy is done. His research deals primarily with information extraction from large astronomical sky surveys and spans the disciplines physics, cosmology, image analysis, machine...
Mysterious cosmic event confirms cutting-edge astrophysics model
Scientists have observed a rare celestial phenomenon that supports a groundbreaking model of black hole behaviour.
Larger galaxies thrive in crowded cosmic neighbourhoods
In a study published in the Astrophysical Journal, researchers from the University of Washington, Yale University, and international partners have uncovered a surprising correlation between a galaxy's size and its cosmic surroundings.
Red dwarf stars emit intense UV radiation
Red dwarf stars can produce stellar flares emitting far-ultraviolet (far-UV) radiation at levels much higher than previously believed.




![How did the first stars form in space? Figure 1: Sketch of the evolution of the Universe over the last 13.77 billion years. It started with the Big Bang, followed by an extremely short period of rapid exponential expansion. The furthest we can see is the cosmic microwave background, when radiation decoupled from matter, approximately 380,000 years after the Big Bang. This is followed by the ‘dark ages,’ during which this radiation redshifted from the visible regime into infrared and sub-mm wavelengths. The occurrence of the first stars, about 400 million years after the Big Bang, ended this phase, spearheading the formation of galaxies as we see them today. [Credit: NASA/WMAP Science Team, public domain]](https://www.openaccessgovernment.org/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/Fig-1_1200-696x464.jpg)