Open Access Government produces compelling and informative news, publications, eBooks, and academic research articles for the public and private sector looking at health, diseases & conditions, workplace, research & innovation, digital transformation, government policy, environment, agriculture, energy, transport and more.
Home Search
astronomy - search results
If you're not happy with the results, please do another search
The mystery of supernova 1181
Chronicles from Japan, China, and Korea documented the sudden appearance of a "guest star" in the heavens, a luminous celestial body visible to the naked eye for approximately 180 days before fading into obscurity.
Citizen scientists discover star on course to escape the Milky Way
Citizen scientists participating in the Planet 9 project have helped uncover a rare and extraordinary star, J1249+36, which is heading through the Milky Way at an incredible speed.
Scientists find fewer miniature black holes in early universe than expected
Researchers at the Research Center for the Early Universe (RESCEU) and Kavli Institute for the Physics and Mathematics of the Universe (Kavli IPMU, WPI) at the University of Tokyo have made a significant breakthrough in our understanding of the early universe.
NASA’s James Webb Telescope maps weather on exoplanet WASP-43 b
Using NASA's James Webb Telescope researchers have revealed insights into the weather patterns of the hot gas-giant exoplanet, WASP-43 b.
Galactic gas outflow: Cosmic fountain leaking into galaxy NGC 4383
A discovery of a gas outflow has been made about the galaxy NGC 4383, located within the Virgo cluster.
Milky Way’s largest stellar black hole revealed 2,000 light years away
The largest known stellar black hole in the Milky Way has been discovered.
Ancient galaxies “Shakti” and “Shiva” were discovered in the Milky Way
Astronomers have identified what could be two of the Milky Way's earliest building blocks, "Shakti" and "Shiva".
Astrophysics research in North America
Open Access Government provides a brief overview of the advancements in astrophysics research in North America.
New insights into exoplanet formation
Astronomers from Germany and Switzerland have revealed evidence of how the gap in the size distribution of exoplanets, particularly those around two Earth radii emerges.
Cosmic dust storms: Supernova sparks new understanding
Astronomers have uncovered a previously unknown mechanism for creating cosmic dust.
New JWST focused study challenges cosmic understanding of the early universe
By analysing data from the James Webb Space Telescope, scientists have uncovered a revelation that could reshape our understanding of the early universe.
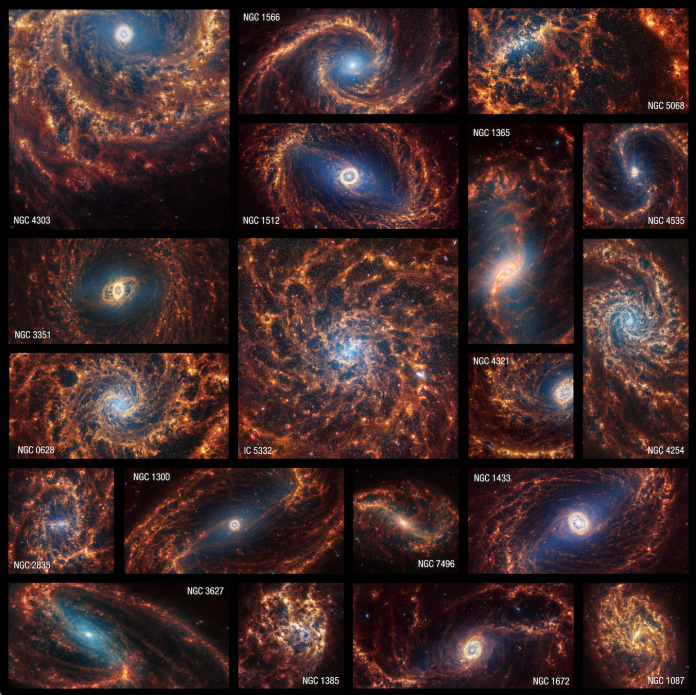
JWST reveals 19 nearby spiral galaxies in stunning clarity
NASA's James Webb Space Telescope has unleashed fascinating images, offering an unprecedented glimpse into the heart of nearby spiral galaxies.
Astronomers locate unknown object within the Milky Way: NGC 1851
Astronomers have discovered a mysterious celestial object in the Milky Way using the MeerKAT Radio telescope.
Astronomers discover an Earth-sized planet in our cosmic backyard
A team of astronomers has identified a planet closer and younger than any other Earth-sized world.
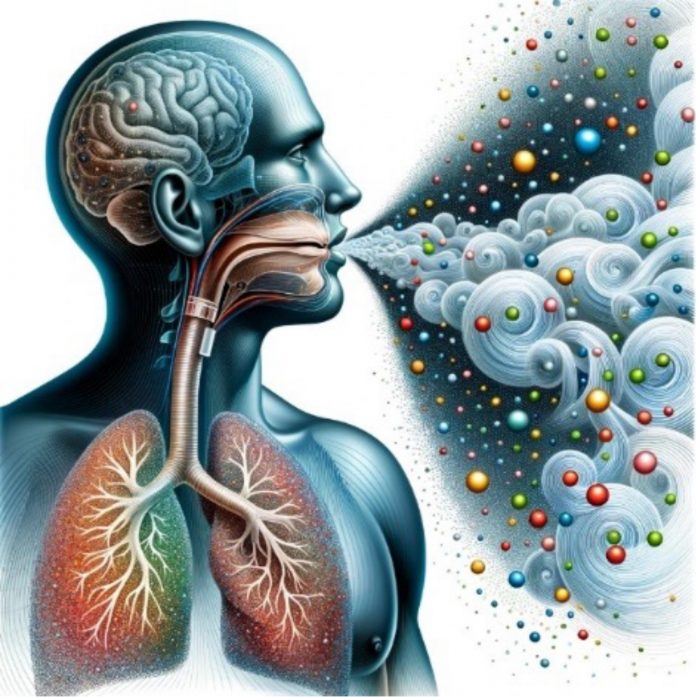
Revolutionising disease detection: The emergence of non-invasive VOC breathomics
Breathomics marks a revolutionary approach to disease detection by analyzing the chemical composition of exhaled breath.
Professor John H. Miller, Jr. – University of Houston
Prof. Miller received his Ph.D. at the University of Illinois in 1985, where he studied the dynamics of charge density waves under the direction of John Tucker and two-time Nobel Laureate John Bardeen.
Prof. Miller was a faculty member in the Department of Physics and Astronomy at the University of...
A ‘Triple Star’ discovery set to revolutionise stellar evolution understanding
A groundbreaking revelation by scientists at the University of Leeds has the potential to reshape astronomers' understanding of some of the largest and most prevalent stars in the universe.
Detecting ancient earth-like planets easier than identifying modern Earth
Scientists at Cornell University suggest that by examining Earth's Phanerozoic era, telescopes could improve the detection of potential signs of life on exoplanets.
Venus’ ancient Earth-like plate tectonics: New possibilities
A recent study suggests that Venus, typically viewed as a fiery wasteland, may have experienced Earth-like plate tectonics in its distant past.
Massive space explosion yields life-sustaining elements
A colossal space explosion, triggered by the merger of two neutron stars, has unveiled the formation of rare chemical elements essential for life.