Home 2024
Archives
Digital Life Norway (DLN) Initiative to foster and boost transdisciplinary biotechnology research and innovation
Meeting the rapid developments in biotechnology by fostering transdisciplinarity, including digitalisation and big data, to create convergence for innovation in a virtual centre.
Removing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere
The agricultural sector plays a decisive role in tackling climate change. GERICS explores what actors of the agricultural sector think of removing carbon dioxide and what support they need from science.
Bio-based solutions for a circular economy
Principal Scientist Ulla Forsström from the VTT Technical Research Centre of Finland Ltd tells us about the INN-PRESSME Open Innovation Test Bed project, which aims to develop novel, sustainable and recyclable bio-based solutions to replace fossil-based plastic.
Microbe development for the biomanufacturing age
Joe Price, Dr Kang Lan Tee & Prof Tuck Seng Wong, explore adopting a holistic approach to microbe development for the age of biomanufacturing.
Purple non-sulfur bacteria and the circular economy
Arpita Bose, Associate Professor at Washington University in St. Louis, discusses the potential of microbial solutions in supporting sustainable and environmentally responsible alternatives to the traditional linear economy.
AI and modern experimental biology: A historical perspective
Ute Deichmann, Director of the Jacques Loeb Centre for the History and Philosophy of the Life Sciences at Ben-Gurion University of the Negev, discusses the adoption and limitations of Artificial Intelligence within modern experimental biology.
FFEA software: Repeated early innovation
Dr Joanna Leng, Senior Research Software Engineering Fellow at the University of Leeds, discusses software with repeated early innovation using the example of the FFEA software.
Harnessing redox power for biotechnological application in purple non-sulphur bacteria
Here we explore purple non-sulfur bacteria (PNSB) and some of its biotech applications, with a focus on how these applications have been enhanced by manipulating the flow of reducing power.
Bio-inspired design approaches to artificial blood technology: Oxygen carriers
Allan Doctor, MD, Professor of Pediatrics at the University of Maryland School of Medicine, shares his expertise on bio-inspired design approaches to artificial blood technology: oxygen carriers.
CB₂R ligands to treat inflammatory diseases
Researchers discuss how scientific innovations might influence the discovery of future tailor-made CB2R-based anti-inflammatory treatments.
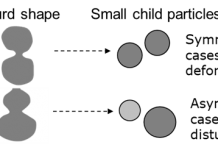
Interdisciplinary research on the splitting process of various particles
Professor Ken Naitoh from the Department of Applied Mechanics and Aerospace Engineering at Waseda University in Japan, walks us through universal laws discovered from outstanding integrated interdisciplinary research on the splitting processes of various particles.
Artificial intelligence (AI) and biomaterials: A perfect BandAId™
Thomas J Webster, Ph.D., Professor and Entrepreneur, is investigating the potential of AI in medical applications and biomaterial production.
Computational biology is poised to advance precision medicine with machine learning
Today, scientists are attempting to model whole cells using computational biology, building virtual cells that capture the dynamics of living.
Microbiome of the skin: The good and the bad
Chronic wounds are a significant burden to patients and health systems; Manuela Martins-Green from the University of California tells us how her research in understanding the dynamics of wound healing could aid new approaches to wound care.
Can we do drug repositioning without disease gene expression?
Chuo University’s Professor Y-h. Taguchi examines the application of cutting-edge single-cell-based measurements in drug repositioning.
Early detection of algal infection using direct real-time chemical ionization mass spectrometry
Robert S. Pomeroy, Teaching Professor at UC San Diego, guides us through the early detection of algal infections using direct real-time chemical ionization mass spectrometry.
Bacteriophages: Nature’s remedy for tackling superbugs and antimicrobial resistance
Given the increasing threat of antimicrobial resistance, Gunther Vanwezer, CEO of Vésale Bioscience, explains how bacteriophages offer a promising natural solution and outlines the company’s efforts to become a pioneer in the development of innovative, personalised and sustainable phage-based therapy solutions.
Decarbonising the world economy with synthetic biology
Macquarie University Distinguished Professor Ian Paulsen, discusses how synthetic biology can be used to decarbonise the global economy.
The role of microbial diversity in microbial electrosynthesis
Bacteria are often painted as the enemy of humanity. Before the discovery of antibiotics, a wound getting infected was frequently a death sentence.
Improving AI/ML services for ophthalmology and medicine
Eric Buckland, PhD of Translational Imaging Innovations, delves into how we can achieve better transparency, traceability, and reproducibility in AI/ML for ophthalmology and medicine.